Having a list of software that is allowed to be installed on a host is a strategy to prevent and fix security gaps and maintain compliance with operational guidelines. This zero-trust methodology ensures that only explicitly permitted applications are allowed to be present on a host unlike package block-listing which enumerates an explicit list of software that is not allowed to be present. In fact, with a software allow-list, you are essentially block-listing everything except the software you allow.
The new packages-allowlist module on CFEngine Build can help you facilitate this.
The packages-allowlist module targets the platforms default package manager and provides an inventory of packages installed that are not in the allow-list (as defined by the packages_allowlist:state.allowed list variable) by default.
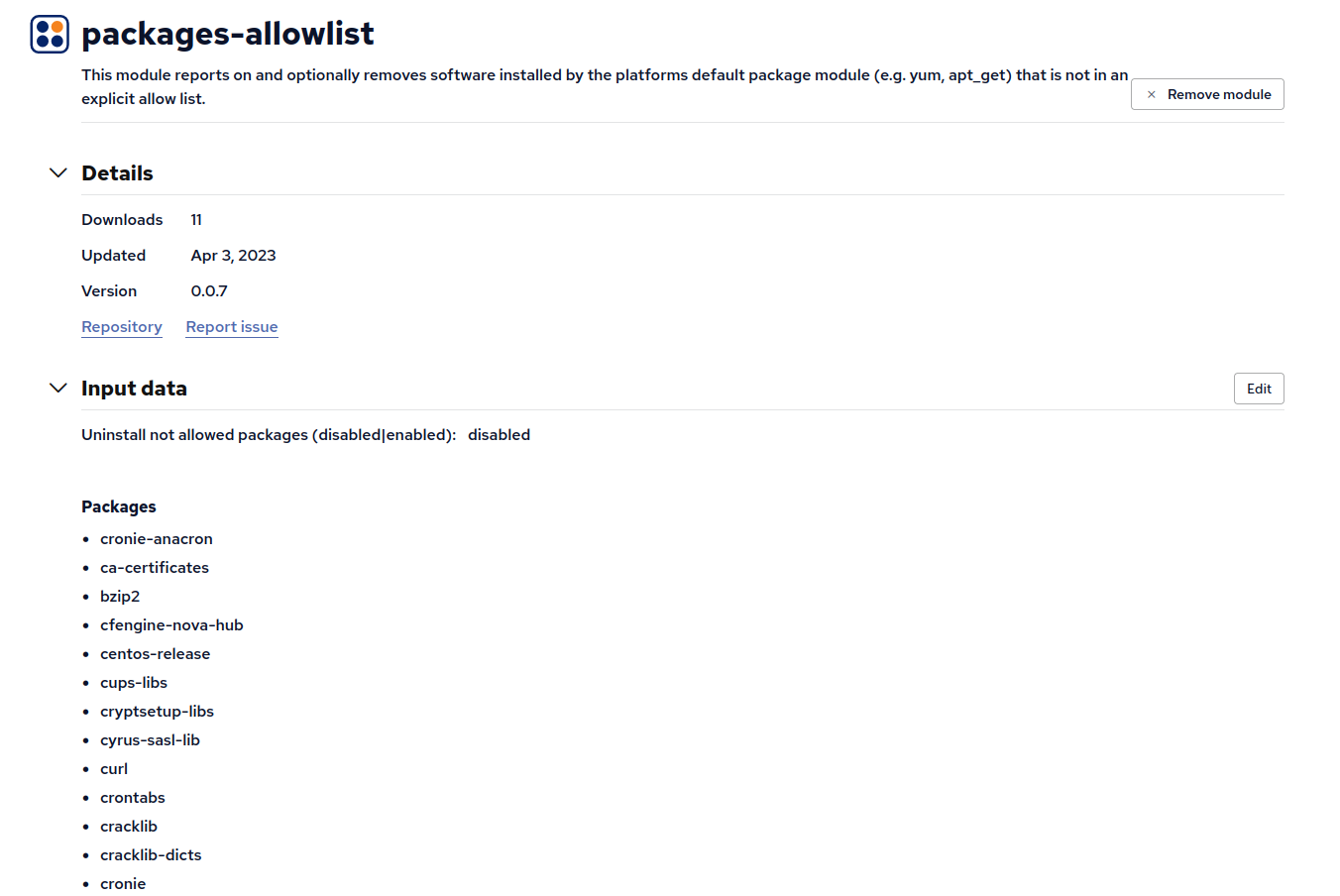
Any packages found installed that are not in the allow-list are inventoried as Packages installed not in allow list.
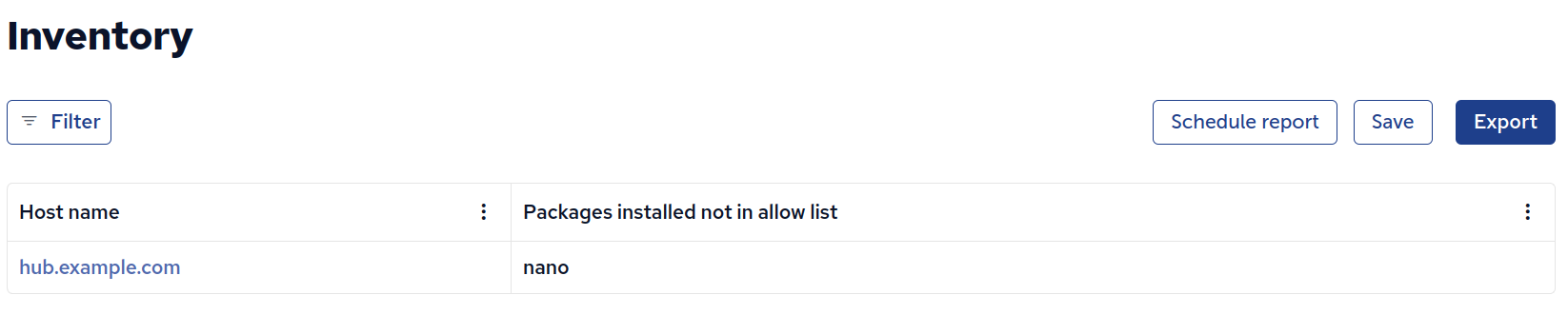
This inventory can be used to build alerts and compliance checks to quickly notify stakeholders of non-compliance.
By default packages_allowlist:state.enforcement is set to disabled. While packages_allowlist:state.enforcement is not enabled warnings are emitted for each package that is not found in packages_allowlist:state.allowed.
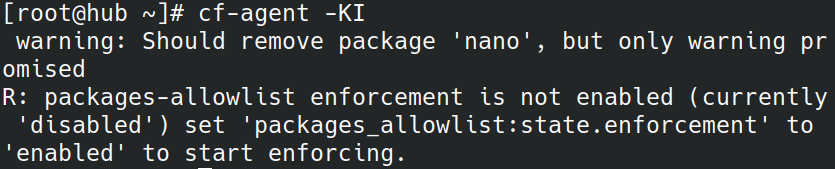
When the variable packages_allowlist:state.enforcement has a value of enabled these packages will be automatically removed.

Try out the module and let us know what you think on GitHub Discussions or on the help mailing list.


